Differences between pasteurization and sterilization
Before discussing pasteurization and sterilization, we should know that the difference between sterilization and pasteurization can be examined from the point of view of definition, function, type, and useful life. Sterilization is a process that destroys all microorganisms and germ eggs. But in the pasteurization method, only the vegetative forms of bacteria are destroyed.
What is pasteurization?
The process that by heating can destroy most of the microbes in food and make them suitable for consumption and eating is called pasteurization. With this method, more than 90 to 99% of microbes in food, including all viruses and bacteria, are destroyed. However, with pasteurization, it is possible to kill 100% of all microbes.
Currently, scientists are able to eliminate a large number of microbes by adjusting the amount of applied heat or the duration of heating. Milk is one of the most important materials that are applied to them by pasteurization. In this process, it should be noted that after the process is finished, the pasteurized materials should be stored in appropriate places. Because these materials will simply be re-contaminated.
Different methods of pasteurization
Two continuous and non-continuous methods are defined to perform pasteurization.
Discontinuous method:
In this method, a long period of time, but a low temperature is used to perform the pasteurization process. For example, milk is heated to 63 degrees Celsius for 30 minutes. This method is considered as the easiest and at the same time the oldest method. By pouring the materials that we intend to pasteurize into large pots, heat is applied to them. During heating, the inside of the boilers is stirred for uniform heat transfer.
Continuous method:
In this way, they use high temperature but short time for pasteurization. For example, milk is heated to seventy-two degrees Celsius for 15 minutes. In the continuous method, which is widely used, it has more economical acceleration and energy consumption compared to the non-continuous method. The source of heat in a non-continuous way is a heat exchanger. The materials that are the goal of the pasteurization process will be placed in a flow opposite to the flow of heating materials with a set temperature and time. After going through this stage, the material cools down quickly.
Attention:
Depending on what kind of food is pasteurized and what is the purpose of pasteurization, different methods are used. For example, in order to better preserve the taste, color and ingredients with edible value, food is used in a non-continuous way. But there are other types of pasteurization methods, which we will discuss some of them, such as pasteurization with steam, with radiation and the UHT process.
Pasteurization using steam:
In this model of pasteurization, which is mainly used for beef pasteurization. For about 6 to 8 seconds, this product is passed through a tank that is located near the high pressure steam. In this method, the temperature used is around 88 to 93 degrees Celsius. After this step, the cooling operation of this product is done by spray method. In America, steam pasteurization methods will be used to pasteurize more than 50% of the meat in this country.
Pasteurization using radiation:
It is possible to pasteurize products such as spices, fruits, vegetables and red meat with the efficiency of radiation technology. By exposing them to a small amount of beta or gamma rays, the growth of microbes in these materials will be prevented. The shelf life of these products will increase with pasteurization.
UHT process:
This pasteurization method is used to pasteurize milk or cream. It is done for these materials with a temperature higher than 138 to 150 degrees Celsius and for a period of one to two seconds.
An important point to be noted here is that pasteurized milk with this high heat method will be able to stay healthy without refrigeration for several months. When the packaging of these milks is opened, their expiration date will be the same as normal pasteurization.
Different types of Pasteurizer
What is sterilization?
Sterilizing is a process that will remove germs and their transmitting agents including fungi, bacteria, bacterial spores and viruses from surfaces.
Autoclavable medical supplies
Most of the medical and surgical devices that are used in hospitals and other healthcare centers are made of materials that have good stability against temperature (autoclavable).
Therefore, exposed to heat, they will be sterilized or disinfected in the first stage of steam. In other words, these appliances have autoclave capabilities.
Definition of cold sterilization
Since the 1950s, medical devices and supplies made of plastic materials that require low-temperature sterilization have grown significantly. As a result, since 1950, ethylene oxide gas has been used to disinfect medical devices and equipment sensitive to heat and humidity. This method of sterilization is called cold sterilization.
Medical devices and equipment that are in contact with body tissues and fluids are among the items that must be sterilized during use. These equipment include: surgical instruments and supplies, biopsy forceps and implanted medical supplies and equipment.
Sterilization in the laboratory
Sterilization methods in laboratories are one of the mandatory points for the health and safety of the environment and personnel. Medical diagnosis laboratories are at risk of contamination due to dealing with various clinical samples such as blood, urine, feces, etc. Each of these samples may carry different types of bacteria, viruses and fungi that cause disease. Things like spilling contaminated samples on laboratory surfaces, breaking containers containing laboratory samples, the presence of aerosols containing contaminated particles in the air may endanger the health of the environment and laboratory personnel. As a result, it is very important to identify the types of sterilization methods in the laboratory.
Physical methods of sterilization:
1. Use of heat
The most accepted and widely used method is heat sterilization. Heat will eliminate the harmful effects and polluting substances of the environment. Heat is used in two ways, dry and wet. Wet heat is more penetrating and effective than dry heat.
2- Humid heat
It is done by an autoclave device and its ability to destroy is much faster than dry heat. It is possible to perform this process in several ways: boiling, water steam and water steam combined with pressure. Autoclave produces steam under pressure. Since the spores are resistant to heat, there is a need for a temperature higher than the boiling point of water in order to destroy them, and this temperature is produced by the autoclave.
3- Dry heat
There is no water in this method. Finally, protein hydrolysis will not happen. In contrast, dry heat tends to kill microbes by oxidizing cellular components.
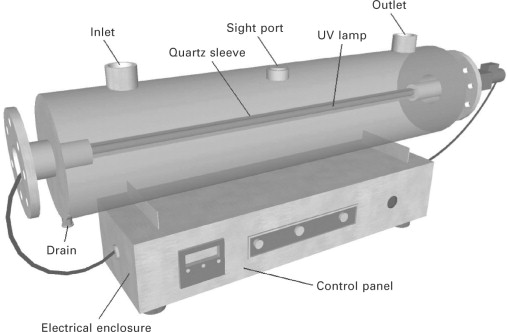
UV Rays
UV rays are deadly. It has the maximum absorption by DNA in the wavelength of 240-280 nm and in the optimal form of 260 nm. This radiation will change the shape of DNA by creating a covalent bond between pyrimidines next to the same strand of DNA and finally forming thymidine dimer. On the other hand, inhibition of DNA synthesis leads to inhibition of bacterial growth and death.
UV rays will have equal effects on gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. In higher doses, it can cause photohydration (breaking of the cytosine molecule) and the formation of a bond between two strands of DNA. Mercury vapor lamps produce this radiation. However, due to the fact that the lifespan of these lamps is limited, it is always necessary to pay attention to the working time of the lamp.
UV rays have the greatest effect on liquids and have no effect on solids. It is used under hoods, laboratories, operating rooms and hospital wards to control airborne infections.
Ionizing Radiation
In certain cases, ionizing radiation can directly cause DNA damage. But its main function is to damage the DNA molecule indirectly. In this way, the ionizing radiation causes the water to break by affecting the water molecules in the environment. The amount of resistance to this radiation depends on the ability to repair DNA.
Spores (the dormant form of bacteria) are one of the most resistant bacteria against ionizing radiation, and after spores, gram-positive bacteria also show resistance to ionizing radiation. This resistance is due to the presence of pigments in bacteria. One of the most important and practical ionizing rays is gamma rays with a dose of 2.5 megarads. This method is used to prepare heat-sensitive liquid products and environments.
Filtration prevents bacteria from entering the environment, but it will not affect viruses due to their extremely small size. The filter pore diameter is different from each other. But the filters that are mainly used. They have a diameter of about 0.22 micrometers. Among these filters, we can mention the air filter, which is used in surgical rooms, isolation rooms, and laboratories. The HEPA filter is used in solutions containing serum, plasma and trypsin, in which the presence of bacteria is high.
Sepyani Industrial Group, together with the most selected Iranian engineers, is ready to provide the services of setting up and installing the dairy production line and designing the pasteurization and sterilization mechanism for your production unit. To learn more about the dairy production line and the role of pasteurization, visit the blog section of our site and read related articles. We are very pleased and grateful that you choose our site to learn about and use the services of industrial processes.
The difference between pasteurization and sterilization
So far, you are familiar with the definitions and methods of pasteurization and sterilization, but what are the differences between them?
Surely by now you have somewhat understood the differences between pasteurization and sterilization. But in the continuation of this topic, we will deal with them case by case and in detail.
1. Loss of materials:
In pasteurization, all bacteria and microscopic organisms will not be destroyed, but in sterilization, everything (bacteria, viruses, active enzymes, and others) will be destroyed. In fact, in the pasteurization process, it is tried to destroy only pathogenic agents by applying optimal heat. But in sterilizing everything that is there will be lost even if it is useful.
2. Temperature in pasteurization and sterilization:
In low heat pasteurization, higher heat is used in sterilization. The reason for this difference is that the preservation of some bacteria is not particularly important in sterilization. As a result, they raise the temperature. So that in a short period of time all microscopic organisms are destroyed and the food is completely cleaned and disinfected.
In sterilization, heat above 100 degrees is used, but in pasteurization, temperatures lower than 100 degrees Celsius are used. Of course, note that chemical methods will also be used in sterilization.
3. Useful life span:
Products that are sterilized have a longer life than pasteurized products. The reason is clear. In sterilizing, all bacteria, viruses and other substances that cause product spoilage will be destroyed. But in pasteurization, not all of them are destroyed and some bacteria will remain.
Certainly, in the pasteurized environment, the conditions for the faster growth of bacteria and more spoilage substances are provided. For this reason, the final product of sterilization has a longer life than the final product of pasteurization.
4. Their application:
Pasteurization is used for utilization in food industries, cultivation environments and medicines. If the method of sterilization includes a wider range and it can be used both in the food industry and in medicine, dentistry and microbiology.
By sterilizing the products in these areas, it is possible to prevent the growth and development of diseases and provide a sterile and healthy environment for the work to proceed. As a result, sterilization has more and wider efficiency and it is used in more fields.
5. Practical methods in pasteurization and sterilization:
In the pasteurization process, in most cases, heat is used to destroy bacteria. But in sterilization or sterilizing, in addition to heat, this work can be done by chemicals. In the chemical method, sterile liquids and gases can be used to destroy microorganisms. and sterilized the desired product or substance.
Conclusion:
The difference between pasteurization and sterilization includes the difference in the destruction of materials, temperature, their efficiency, the useful life of the products, and the methods. In pasteurization, all microscopic materials (bacteria, viruses, fungi, etc.) will not be destroyed, they are less useful, the temperature is lower, the useful life of the product is less, and the method of doing them is almost exclusively in heating.
If higher heat is used in sterilization, all fine material will be destroyed. The useful life of the product is longer, they are more effective, and apart from heat, they also use liquid and chemical gas to sterilize products, surfaces, and the environment. For more information, complete consultation request form. You can also contact us through What’sApp.