DCS system
In recent years, the use of smart devices has made the Distributed Control System (DCS) prominent in large and complex industrial processes compared to the former centralized control system. This distribution of control system architecture around the plant has resulted in more efficient ways to improve control reliability, process quality and plant efficiency. Today, the distributed control system is used in many industrial fields such as chemical factories, oil and gas industries, food processing units, nuclear power plants, water management systems, automotive industries, etc.
DCS system design
A DCS (distributed control system) is an automated control system designed to consist of geographically distributed control elements over a plant or control area. This is different from a centralized control system where a controller at a central location handles the control function.
But in DCS each process element or machine or group of machines is controlled by a dedicated controller. DCS consists of a large number of local controllers in different parts of the power plant control area and are connected through a high-speed communication network.
Communication of Microcontrollers
In the DCS control system, data collection and control functions are performed through a number of DCS controllers that are microprocessor-based and functionally and geographically distributed on the power plant.
These units are located near the area where control or data collection functions are performed. These controllers can communicate among themselves as well as with other controllers such as supervisory terminals, operator terminals, historians, etc.
Connecting Microcontrollers
Individual distributed automation controllers are connected to field devices such as sensors and actuators. These controllers ensure the sharing of collected data with other hierarchical controllers through various fieldbuses. Different fieldbuses or standard communication protocols are used to communicate between controllers. Some of these include Profibus, HART, arc net, Modbus, etc.
DCS is suitable for processing plants or large-scale production. Because in such factories, a large number of continuous control loops must be monitored and controlled. The main advantage of dividing control tasks for distributed controllers is that if any part of the DCS fails. The plant can continue to operate regardless of the damaged part.
DCS system architecture
As the name suggests. DCS has three main features. The first is the distribution of various control functions into relatively small sets of subsystems that are semi-autonomous. And they are connected through a high-speed communication bus. The second feature of DCS is the automation of the manufacturing process by integrating advanced control strategies.
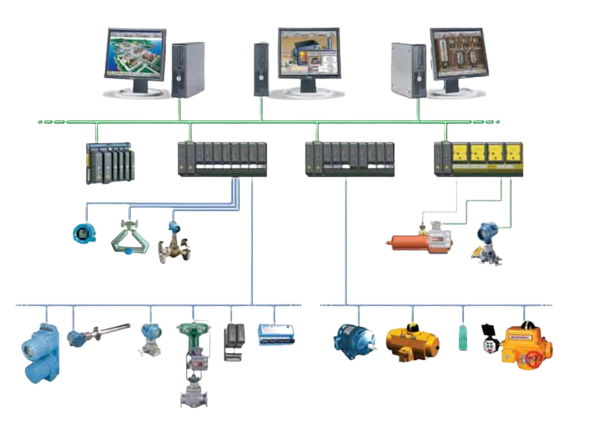
DCS organizes the entire control structure as a single automation system in which the various subsystems are unified through an appropriate command structure and information flow. The basic elements in a DCS include engineering workstation, operating station or HMI, process control unit or local control unit, intelligent devices and communication system.
DCS engineering workstation
This is a supervisory controller for the entire distributed control system. It can be a PC or any other computer that has dedicated engineering software. For example, the control engineering station F. This engineering station offers powerful configuration tools. This unit allows the user to perform engineering functions such as creating new loops, creating different input and output points, modifying sequential control logic, configuring different distributed devices, preparing documentation for each input/output device, etc.
Operating Station or HMI
This unit is used to operate, monitor and control plant parameters. It can be a personal computer or any other monitoring device that has a separate software tool that the operator can view the values of the process parameters. Take control measures accordingly. For example, DigiVis is a software tool that can run on a simple PC environment in the case of an ABB DCS. Operating stations can be one unit or multiple units, where one unit performs functions such as parameter value display, trend display, alarm, etc. While several units or PCs have separate functions such as some PC display parameters, some for process archiving, some for recording and receiving data, etc.
DCS process control unit
Also called as local control unit, distribution controller or process station. A DCS system can consist of one or more process stations. This station can be expanded with different types of I/O units. These controllers consist of a powerful CPU module, fieldbus or communication module with extended fieldbus capability and directly or remotely connected I/Os.
Field devices such as sensors and actuators are connected to the input/output modules of this unit. Some field devices can be directly connected to the fieldbus (such as Profibus) without an I/O module, which can be called smart field devices.
These units obtain information from various sensors through the input module. They analyze and process it and send output signals through output modules to control actuators and relays.
Communication System
The communication medium plays the main role in the whole DCS system. It connects engineering station, operating station, process station and smart devices. It transfers information from one station to another. Common communication protocols used in DCS are: Ethernet, Profibus, Foundation Fieldbus, DeviceNet, Modbus, etc.
It is not mandatory to use one protocol for the entire DCS. Some levels can use the same network while some levels use different networks. The main advantage of DCS is the redundancy of some or all control area levels. Most critical processes are installed with redundant controllers and redundant communication networks so that a problem in the main processing line due to the redundant processing part should not affect the monitoring and control functions.
Smart field devices
Intelligent field devices and fieldbus technology are advanced features of DCS technology that replace traditional I/O subsystems (I/O modules). These smart devices embed the intelligence needed for simple measurement and control techniques in the basic sensor and actuator devices. Hence, it replaces the need for a DCS controller to perform the conventional sensing and control process. These field devices can be connected directly to the field bus to enable multiple measurement sources to the next higher level control station via a digital transmission line, eliminating additional hardware such as local I/O modules and controllers.
Operation of DCS system
The function of DCS is that the sensors sense the information of the process. It is sent to the local I/O modules. This is while actuators are also connected to them to control process parameters. The information or data of these remote modules are collected to the process control unit through the fieldbus, and if smart field devices are used, the sensed information is directly transferred to the process control unit through the fieldbus.
The collected information is further processed, analyzed and produces output results based on the control logic implemented in the controller. Then the control results or actions are transmitted to the driving devices through the field bus. Configuration, setup and execution of the DCS control logic is done at the engineering station as mentioned earlier. The operator can view and send control actions manually at the operation stations.
Difference between SCADA and DCS
Although DCS and SCADA are both monitoring and control mechanisms in industrial facilities. But they have different goals. There are some similarities between DCS and SCADA in terms of hardware and components. However, there are specific requirements by end applications that separate a robust and cost-effective DCS from a viable SCADA system. Here are some differences between DCS and SCADA:
DCS vs. SCADA
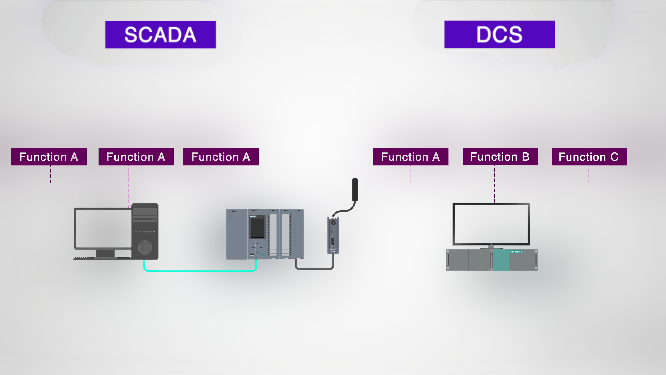
- One: DCS is process oriented while SCADA is data collection oriented.
- Two: DCS focuses more on process control and also includes a level of supervisory control. It also provides information to the operator as part of doing so. SCADA, on the other hand, focuses more on acquiring process data and presenting it to operators and the control center.
- Three: In DCS, data collection and control modules or controllers are usually located in a more limited area and communication between different distributed control units is done through a local area network. SCADA generally covers larger geographic areas that use different communication systems. These systems are usually less reliable than a local network.
- Four: DCS uses a closed-loop control at the process control station and at remote terminal units, but SCADA does not have such a closed-loop control.
- Five: It should be noted that the DCS has a process mode where it scans the process regularly and displays the results to the operator even on demand. But SCADA is event driven. Where it doesn’t scan the process sequentially. But it waits for an event that causes the process parameter to initiate certain actions.
- Six: In terms of applications, DCS is used for installation in a limited area, such as an industrial automation or unit plant, and for complex control processes. Some of the application areas of DCS include chemical plants, power plants, pharmaceutical manufacturing, oil and gas industries, etc. Applications and small manufacturing and process industries.
DCS or SCADA?
Despite these major differences, modern DCS and SCADA systems come with common standard features when working with factory automation. However, the choice between DCS and SCADA depends on the needs of the customer and its final application. But if the customer hesitates between these two choices. DCS is the economical choice as it helps to reduce cost and provide better control.
Some of the DCS systems available are:
- ABB- Freelance 800F and 800 xA
- Yokogawa- Centum CS 3000 and 1000
- Honeywell-TDC 3000
- Emerson-Delta V digital automation
- Siemens industrial automation – Simatic PCS 7
- Allen-Bradley-Net Linux
Conclusion:
Sepyani Industrial Group is active in the field of industrial automation, plc industrial automation, Siemens industrial automation, as well as designing and setting up production lines.
To get more information, you can complete the consultation request form so that our technicians will contact you as soon as possible. Also, in order to obtain all kinds of industrial equipment related to industrial electricity, industrial automation, precise tools, pneumatics, etc. you can visit our shop section and inquire about the price. Plus you can contact us by What’sApp messenger.